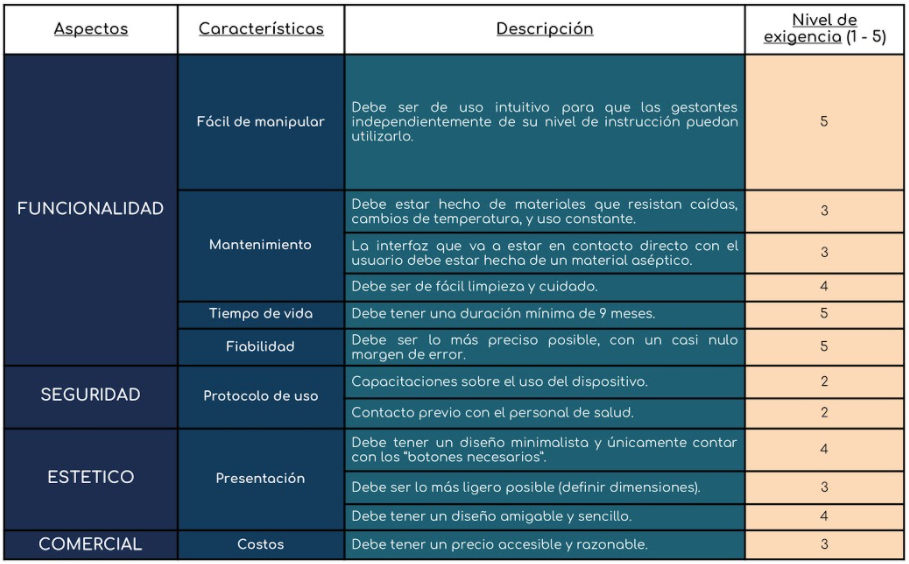
Lista de Requerimientos

[1] J. Kolarik, M. Golembiovsky, T. Docekal, R. Kahankova, R. Martinek, and M. Prauzek, “A Low-cost Device for Fetal Heart Rate Measurement,” IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2018.07.116.
[2] P. H. Crispín Milart, C. A. Diaz Molina, I. Prieto-Egido, and A. Martínez-Fernández, “Use of a portable system with ultrasound and blood tests to improve prenatal controls in rural Guatemala,” Reprod. Health, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 1–8, 2016, doi: 10.1186/s12978-016-0237-6.
[3] D. Ç. Ertuǧrul, H. Kanmaz, M. U. Yüksel, A. Elçi, and M. Ertuǧrul, “Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring System (FHRMS),” 2016, doi: 10.1109/COMPSAC.2016.116.
[4] B. L. Rojas-Mezarina, F. Inga-Berrospi, L. Trujillo, and B. Castañeda Aphan, “Modelo innovador de tele-ecografía para zonas rurales en el Perú,” An. la Fac. Med., 2018, doi: 10.15381/anales.v79i1.14596.
[5] Medical Innovation & Technology, Tele-ecografía para zonas rurales. 2017.
[6] E. Chandraharan, S. Evans, D. Krueger, S. Pereira, S. Skivens, and A. Zaima, “Guía de monitorización fetal intraparto basada en fisiopatología,” Physiol. CTG Interpret., 2018.
[7] ABN Fetal Stethoscope PS-181-BK Rp 200.000. 2012.
[8] N. Barrena M. and J. Carvajal C., “Evaluación fetal intraparto. Análisis crítico de la evidencia,” Rev. Chil. Obstet. Ginecol., 2006.
[9] K. H. Tan, R. M. D. Smyth, and X. Wei, “Fetal vibroacoustic stimulation for facilitation of tests of fetal wellbeing,” Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2013, doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002963.pub2.
[10] W. Schmidt, R. Boos, J. Gnirs, L. Auer and S. Schulze, Fetal behavioural states and controlled sound stimulation. 1985.
[11] O. García and B. Arana, Monitoreo Fetal, Basado en Evidencia. Grupo de Especialistas del Hospital de Gineco Obstetricia - IGSS, 2014.
[12] "Fetal Monitoring", Stanford Children's Health, 2020. [Online]. Available: https://www.stanfordchildrens.org/es/topic/default?id=fetalmonitoring-90-P05558. [Accessed: 19- Sep- 2020].
[13] Tecnomed 2000, Doppler Fetal portátil con pantalla y resistente al agua.
[14] MedlinePlus, Monitorización fetal interna. 2010.
[15] J. Runkle, M. Sugg, D. Boase, S. L. Galvin, and C. C. Coulson, “Use of wearable sensors for pregnancy health and environmental monitoring: Descriptive findings from the perspective of patients and providers,” Digit. Heal., 2019, doi: 10.1177/2055207619828220.
[16] S. Kuang et al., "Functional electrical stimulation device for relieving preoperative and prenatal anxiety and usage method therefor", WO2019113988, 2019.
[17] A. Stuart, P. Kunovski, and S. Samuels, “Movement sensor and garment,” 2019.
[18] H. Jiexin, “Remote fetal monitoring method and system,” 2015.
[19] N. Amrish, A. Diane Davis, N. Vilasini, and T. Sihem, “An apparatus for acquiring signals from a pregnant subject,” 2020.
[20] M. Mhajna et al., “Wireless, remote solution for home fetal and maternal heart rate monitoring,” Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. MFM, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2020.100101.
[21] A. Houzé de l’Aulnoit et al., “Development of a Smart Mobile Data Module for Fetal Monitoring in E-Healthcare,” J. Med. Syst., vol. 42, no. 5, pp. 1–7, 2018, doi: 10.1007/s10916-018-0938-1.
[22] National Intellectual Property Administration, "Portable Maternal And Infant Electrocardiogram Monitoring Device For Parturient", 211187230 U, 2019.
[23] Intellectual Property Office, "AI Pregnancy And Baby Caring Device", M586430, 2019.